S.2.1 System
S.2.1 system we call TECHCODE RFID cabinets and cabinet sets with basic capabilities, allowing remote management and operation of individual users and their groups in several usage schemes.
The following components can work in the S.2.1 system:
Multi-compartment cabinets
Szafy aktowo-narzedziowe
Clothing lockers

Take your company's security to a whole new level and further restrict unwanted access to company secrets.
The S.2.1 system, fitted with clothing, multi-compartment or filing and tool cabinets, is an effective solution for protecting any objects that could fall into the wrong hands.
This is possible thanks to the remote management of the identification process necessary for its users to gain access to the lockers or drawers.
The TECHCODE RFID cabinet with the S.2.1 System operates in single mode and can be managed remotely via LAN input. The System can be equipped with multiple TECHCODE RFID cabinets and offers several operating schemes.
The following cabinets can be equipped with the S.2.1 system:
Clothing
Multi-compartment
File cabinets with drawers
File and tool
Key cabinets

System administrator (A)
The TECHCODE RFID cabinet in the S.2.1 system requires management by the Administrator.
Their duties include entering specific data into the System (e.g. User data), granting rights to individual Users and the ongoing administration of TECHCODE RFID cabinets (e.g. remote opening or releasing of reserved compartments, receiving information on faults, etc.).
Identification and authorisation
The S.2.1 system requires the identification (authorisation) process to be passed correctly before access to the locker, compartment, drawer is granted.
It allows individual media or PIN codes to be assigned to each user and provides different identification modes, depending on the administrator's choice.
Depending on the mode, the user may be required to use one or more identification methods.
User (U)
The use of the TECHCODE RFID cabinet with the S.2.1 system is allowed only for Users defined in the System by the Administrator.
The administrator can add a user to the database by providing personal or identifying data, such as order number, position, department name, room number.
A user can also be assigned to a User Group(s).
Master user (M)
The System Administrator may grant special Master Privileges to a System User, authorising them to perform functions reserved for them.
The System Administrator can be assigned Master Rights at the same time.
User group (UUU)
User groups are structures with specific rights, set by the administrator.
Users assigned to several groups have the rights of all the groups to which they are assigned.

ACCESS CONTROL
and process automation in S.2.1
with TECHCODE RFID cabinets
The TECHCODE RFID cabinet operating in the S.2.1 System, requires management by the System Administrator (A). The S.2.1 System is managed remotely, via encrypted LAN communication (Ethernet or Wi-Fi), using dedicated software available through:
A web-based application operated from a web browser.
Mobile app - operated from Android or IOS mobile devices.
In the S.2.1 System Administrator, it is possible to assign Rights to:
- User
- Defined items/equipment (e.g. a package marked with a QR code)
- User IDs
- Groups to which the User belongs
- User ID groups.
The User's rights may therefore arise from:
Assignment of individual Rights to a User
Assignment of a User to a User Group that has defined Rights
Assignment of individual Rights to the User ID
Assignment of Rights groups to the User ID.
Definition of rights by the S.2.1 system administrator
The S.2.1 system allows basic and advanced rights to be defined, such as opening specific compartments in different ways, allowing access to several compartments for one user, and programming several identifiers to one compartment. The rights can include groups of functions.
During the authorisation process, the system checks:
the rights assigned to the logged-in ID, the user and the groups to which the user belongs. The rights are aggregated.
1. The use of different carriers, such as:
- Contactless cards,
- PIN codes,
- Biometric data.
2. The use of mobile devices, such as Android or iOS phones. In this case, the phone acts as an identifier. Once authorised, the System automatically performs actions in accordance with the identification method assigned (e.g. the card or PIN in question), and in accordance with the rights assigned to the user.
The user has a choice of different means of identification, assigned individual rights (e.g. card A assigns different rights to the user than card B or a PIN code).
The rights to actions in the S.2.1 System depend on the user's activity and can be granted by the System Administrator as personalised rights covering groups of functions.
All individual and group rights are aggregated and the user can only perform those actions for which he or she has rights.
TECHCODE RFID cabinets in the S.2.1 system are operated by a reader to which a card must be applied or a PIN code entered. A common reader allows access to compartments/cabinets, while groups of cabinets are operated by separate readers.
Database types supported by the System:
- Server database - allows multiple Administrators to manage the System,
- File database - designed for small installations, no remote administration required.
The system continuously records events in its database, which is available for download in the history. If there is no connection to the communication server, the controllers record events in internal memory buffers.
Cabinets that can operate in this system

These cabinets are also known as the following cabinets:
- Deposit
- Breakfast
- Clean clothing
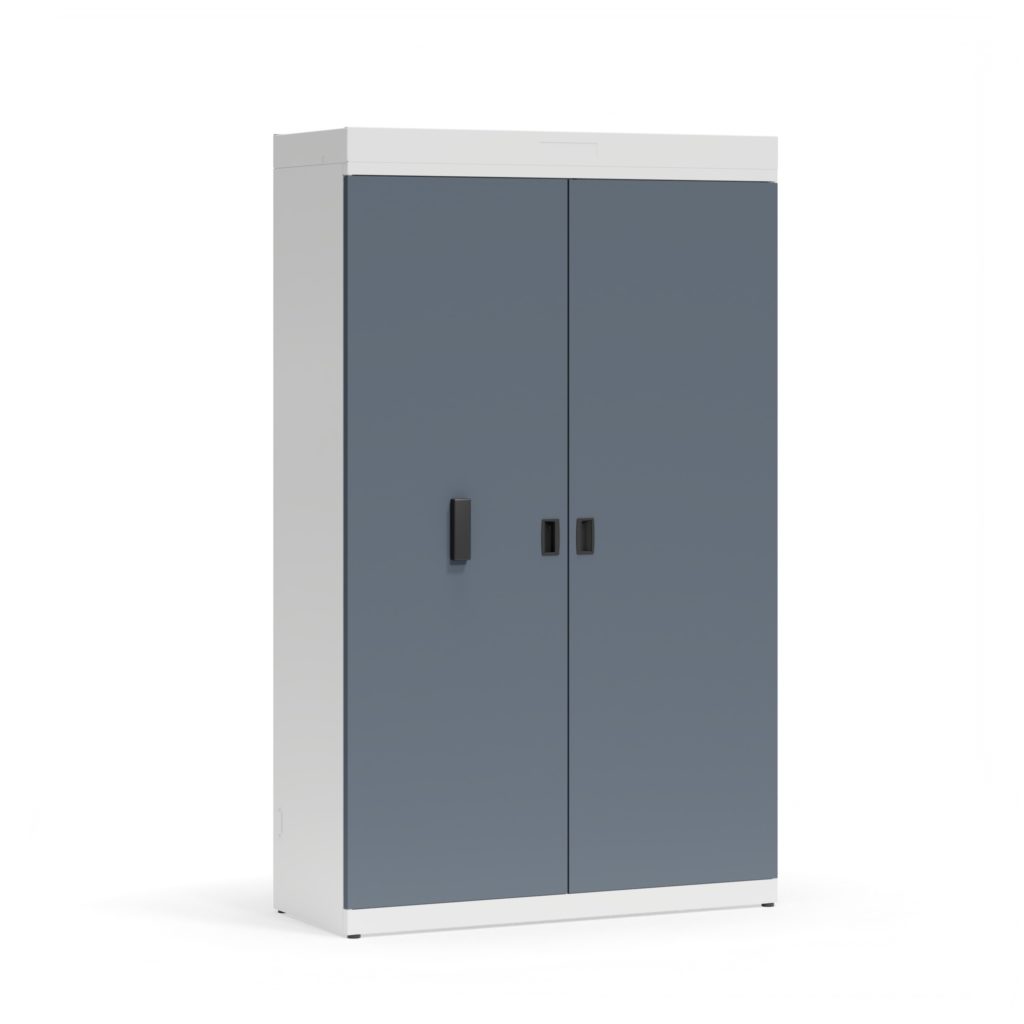

The cabinets allow storage of documents and other resources such as workshop tools.
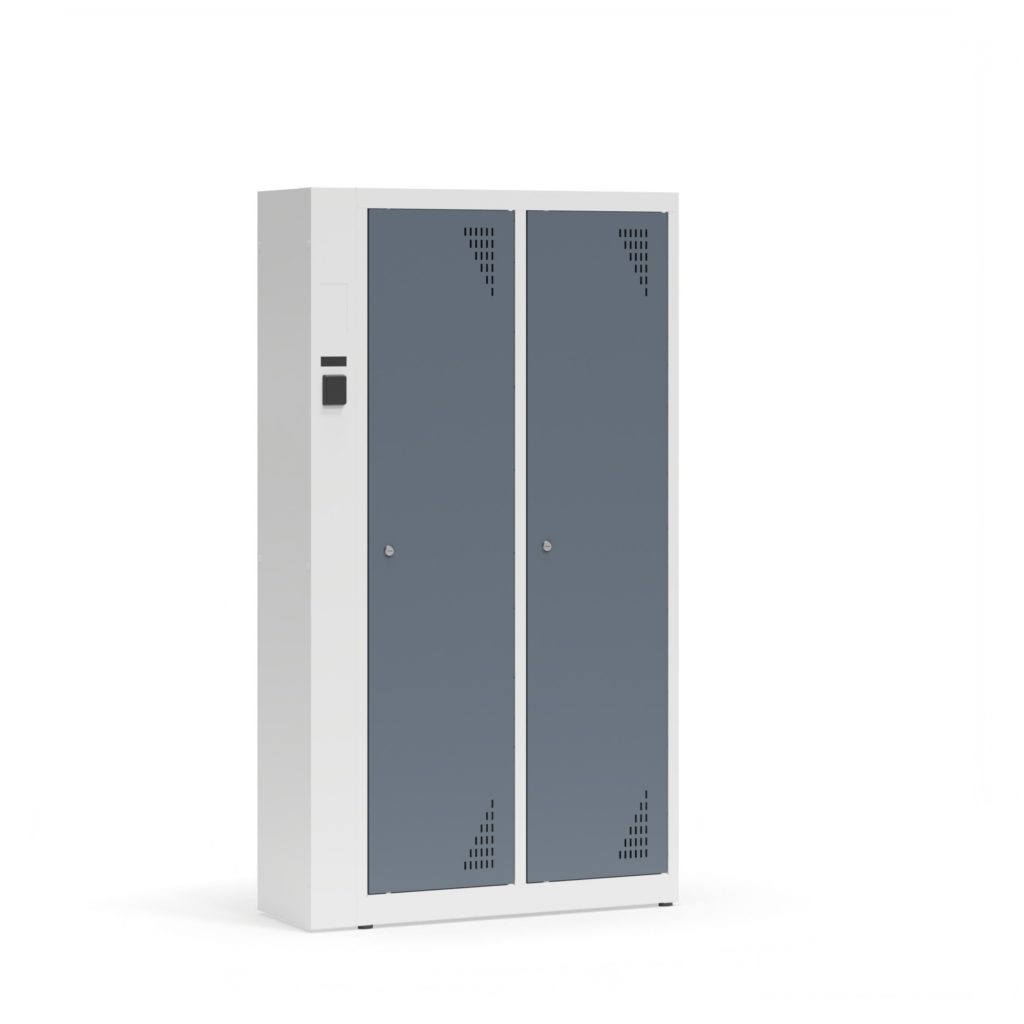

Lockers are used to store clothes and other items in staff changing rooms, hotels, hospitals and sports facilities.

Cabinets for depositing keys and documents are usually fitted out in car service and rental shops, but also in hotels, for example.
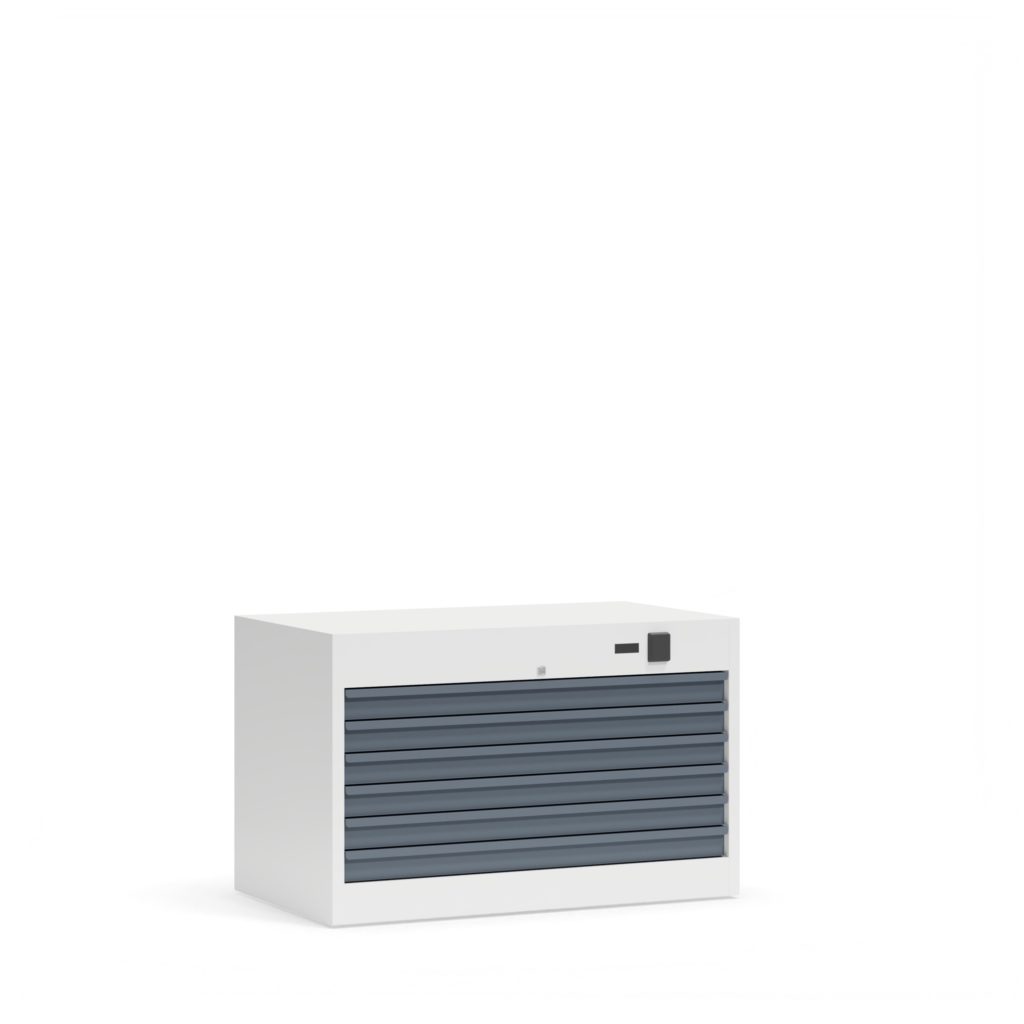

Cabinets with drawers for the secure storage of maps, drawings, paintings and other valuable artefacts in museums, for example.
A TECHCODE RFID multi-compartment cabinet operating in the S.2.1 System can operate in one Mode of operation, in several schemes (using the TECHCODE RFID multi-compartment cabinet with the S.2.1 System as an example):
S.2.1 system - operating scheme 1: UN/1A
The administrator defines:
• User (e.g. Adam Nowak) and the way in which he will be identified in the system (e.g. by telephone, etc.).
• A carrier (e.g. a 121 contactless card) to be used by a user (e.g. a visitor)
and assigns specific rights* to them, e.g. to open a specific compartment.
The system identifies:
• the user by means of the verification method assigned to them (e.g. by telephone)
• the carrier (e.g. 121 card) used by the user and authorises their access to the cabinet
After positive authorisation, the system automatically performs the action assigned to:
• The user in question
• The carrier in question (e.g. card 121)
The action performed will be recorded and assigned by the system to:
• the user assigned to the carrier
• the carrier used by the user
S.2.1 system - operating scheme 2: UN/1HA
The administrator defines:
• User (e.g. Adam Nowak) and the way in which he will be identified in the system (e.g. by telephone, etc.).
• A carrier (e.g. a 121 contactless card) to be used by a user (e.g. a visitor)
and assigns to them the authorisation to temporarily open a specific compartment. Once the time set by the administrator in the system has expired, the granted authorisation expires.
The system identifies:
• the user by means of the verification method assigned to them (e.g. by telephone)
• the carrier (e.g. 121 card) used by the user
and authorises their access to the cabinet
After positive authorisation, the system automatically performs the action assigned to:
• The user in question
• The carrier in question (e.g. card 121)
The action performed will be recorded and assigned by the system to:
• the user assigned to the carrier
• the carrier used by the user
S.2.1 system - operating scheme 3: UN/123UN
The administrator defines:
• User (e.g. Adam Nowak) and the way in which he will be identified in the system (e.g. by telephone, etc.).
• A carrier (e.g. a 121 contactless card) to be used by a user (e.g. a visitor)
and assigns them specific rights, e.g. to select one compartment from a group of compartments made available to them
The system identifies:
• the user by means of the verification method assigned to them (e.g. by telephone)
• the carrier (e.g. 121 card) used by the user
and authorises their access to the cabinet
After successful authorisation, the user selects the compartment to be opened. The action triggered by the user for which the user was authorised is executed automatically.
The action performed will be recorded and assigned by the system to:
• the user assigned to the carrier
• the carrier used by the user
S.2.1 system - operating scheme 4: UN/123UN
The administrator defines:
• User (e.g. Adam Nowak) and the way in which he will be identified in the system (e.g. by telephone, etc.).
• A carrier (e.g. a 121 contactless card) to be used by a user (e.g. a visitor)
and assigns them the authorisation to temporarily open (from a group of shared compartments) a compartment of their choice. After the expiry of a period of time set in the system by the administrator, the granted authorisation expires.
The system identifies:
• the user by means of the verification method assigned to them (e.g. by telephone)
• the carrier (e.g. 121 card) used by the user
and authorises their access to the cabinet
or the carrier
After successful authorisation, the user selects the compartment to be opened. The action triggered by the user for which the user was temporarily authorised is executed automatically.
The action performed will be recorded and assigned by the system to:
• the user assigned to the carrier
• the carrier used by the user
S.2.1 system - operating scheme 5: UUUNNN/1A
The administrator defines:
• Users and methods by which they will be identified in the system (e.g. by telephone, etc.).
• Carrier to be used by users (e.g. visitors)
and assigns specific rights to them, e.g. to open a specific compartment.
The system identifies:
• Users by means of the verification methods assigned to them
• Carriers used by users
and authorises their access to the cabinet
or the carrier
After positive authorisation, the system automatically performs the action assigned to:
• Users
• Carriers
Each action is recorded and assigned by the system to:
• the user identified by the system before the action is performed
• the carrier identified by the system before the action is performed.
S.2.1 system - operating scheme 6: UUUNNN/1HA
The administrator defines:
• Users and methods by which they will be identified in the system (e.g. by telephone, etc.).
• Carriers to be used by users (e.g. visitors)
and assigns specific rights to them, e.g. to temporarily open a specific compartment.
The system identifies:
• Users by means of the verification methods assigned to them
• Carriers used by users
and authorises their access to the cabinet
or the carrier
After positive authorisation, the system automatically performs the action assigned to:
• Users
• Carriers
Each action is recorded and assigned by the system to:
• the user identified by the system before the action is performed
• the carrier identified by the system before the action is performed.
S.2.1 system - operating scheme 7: UUUNNN/1HA
The administrator defines:
• Users and methods by which they will be identified in the system (e.g. by telephone, etc.).
• Carriers to be used by users (e.g. visitors)
and assigns specific rights to them, e.g. to temporarily open a specific compartment.
The system identifies:
• Users by means of the verification methods assigned to them
• Carriers used by users
and authorises their access to the cabinet
or the carrier
After successful authorisation, the user selects the compartment to be opened. The action triggered by the user for which the user was authorised is executed automatically.
Each action is recorded and assigned by the system to:
• the user identified by the system before the last action is performed
• the carrier identified by the system before the last action is performed.
S.2.1 system - operating scheme 8: UUUNNN/123HUN
The administrator defines:
• Users and methods by which they will be identified in the system (e.g. by telephone, etc.).
• Carriers to be used by users (e.g. visitors)
and assigns them the authorisation to temporarily open (from a group of shared compartments) a compartment of their choice.
The system identifies:
• Users by means of the verification methods assigned to them
• Carriers used by users
and authorises their access to the cabinet
or the carrier
After successful authorisation, the user selects the compartment to be opened. The action triggered by the user for which the user is temporarily authorised is executed automatically.
Each action is recorded and assigned by the system to:
• the user identified by the system before the last action is performed,
• the carrier identified by the system before the last action is performed.

